JSON数据格式简介
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级、易于阅读和编写的半结构化数据格式。它基于JavaScript的一个子集,但是JSON是独立于语言的,许多编程语言都有JSON数据格式的解析和生成代码。JSON格式使用文本表示简单的数据结构,如对象、数组、字符串、数字和布尔值。JSON格式具有良好的可读性和简洁性,使其成为理想的数据交换格式。
LakeHouse中的JSON类型
在LakeHouse中,JSON类型的数据可以高效地存储和查询。JSON数据在LakeHouse中会被解析,并根据数据的实际结构进行优化存储。以下是LakeHouse中JSON类型的一些特点:
- 查询性能:使用JSON类型相比于String类型在查询性能上有明显优势,因为LakeHouse会对JSON数据进行列裁剪,减少不必要的数据扫描。
- 数据重排:解析过程中,JSON对象的数据可能会被重新排序,因此输入和输出的JSON数据可能在键的顺序上不一致。
- 数字解析:解析JSON数字时,LakeHouse会优先尝试将其解析为bigint类型。如果数字超出bigint的范围,则会将其解析为double类型。需要注意的是,double类型可能会有精度损失。
- 错误处理:使用函数解析JSON数据时,LakeHouse会进行校验。对于非法的JSON字符串,会返回NULL值;而在声明JSON常量时,非法的JSON字符串会导致错误。
此外,LakeHouse在写入过程中会根据实际的JSON Schema,将出现频次高的字段按照列存储的方式存储,以提高存储和查询效率。例如:
CREATE TABLE json_table AS
SELECT parse_json(s) as j
FROM VALUES
('{"id": 1, "value": "200"}'),
('{"id": 2, "value": "300"}'),
('{"id": 3, "value": "400", "extra": 1}'),
('{"value": "100"}') as t(s);
- 对于上面的数据,LakeHouse 检测出 id 和 value 出现频次高,分别适合用 bigint 和 string 类型列式存储,则会在内部以类似 struct<id:bigint, value:string> 的结构存储。在后续的查询过程中,如果只读取id字段且转换为bigint,如
SELECT json_extract_bigint(j, '$.id'),则可以直接按列读取 id 字段,并消除类型转换的开销。
- 对于出现频次低的 extra 字段,则保留 json 结构且用更加紧凑的表示存储,避免产生过于稀疏的数据。
限制
- 不支持对JSON类型的比较操作,也不支持对JSON类型进行
ORDER BY、GROUP BY或作为JOIN的key等。
- 不支持作为cluster key、primary key、partition key
- JSON字符串最大长度为16 MB。批量、实时导入时对字段进行长度校验。如果您导入数据时有大于16MB的数据您可以修改表的Properties来修改如下将json长度设置为32MB
ALTER TABLE table_name SET PROPERTIES("cz.storage.write.max.json.bytes"="33554432");
创建JSON列的表
要创建包含JSON类型列的表,可以使用以下SQL语句:
CREATE TABLE json_example
(
id bigint,
data json
);
构建JSON数据
JSON常量
在SQL查询中,可以使用JSON常量来表示JSON数据。例如:
SELECT
JSON 'null',
JSON '1',
JSON '3.14',
JSON 'true',
JSON 'false',
JSON '{"id":11,"name":"Lakehouse"}',
JSON '[0, 1]';
-- !query output
+-------------+----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+-------------------------------------+---------------+
| JSON 'null' | JSON '1' | JSON '3.14' | JSON 'true' | JSON 'false' | JSON '{"id":11,"name":"Lakehouse"}' | JSON '[0, 1]' |
+-------------+----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+-------------------------------------+---------------+
| null | 1 | 3.14 | true | false | {"id":11,"name":"Lakehouse"} | [0,1] |
+-------------+----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+-------------------------------------+---------------+
语法
--键名访问JSON对象中的字段
json_column['key']['key']...
--通过索引访问JSON数组中的元素
json_array[index]
参数说明
- json_column:表示一个JSON字段,类型为JSON对象。通过键名(
key),指定为字符串,来定位并检索JSON对象内的特定数据字段。使用单个方括号[]可以访问对象的一级字段;而嵌套使用双方括号[][]则能够深入检索对象的二级或更深层次的字段。
- json_array:数组类型的JSON,用来根据index访问 JSON array的元素,起始值为0
案例
取出json一级结构
SELECT parse_json(s)['firstName'] as j
FROM VALUES ('{ "firstName": "John", "lastName": "doe", "age": 26, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [] } ] }'),
('{ "firstName": "Ada", "lastName": "doe", "age": 20, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "address2": {"city": "NewYork"}, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [1,2,3] } ] }')
as t(s);
取出json二级结构
SELECT parse_json(s)['address']['streetAddress'] as j
FROM VALUES ('{ "firstName": "John", "lastName": "doe", "age": 26, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [] } ] }'),
('{ "firstName": "Ada", "lastName": "doe", "age": 20, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "address2": {"city": "NewYork"}, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [1,2,3] } ] }')
as t(s);
取出json数组中的元素
SELECT parse_json(s)['phoneNumbers'][0]['number'] as j
FROM VALUES ('{ "firstName": "John", "lastName": "doe", "age": 26, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [] } ] }'),
('{ "firstName": "Ada", "lastName": "doe", "age": 20, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "address2": {"city": "NewYork"}, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [1,2,3] } ] }')
as t(s);
使用函数
使用函数(将STRING格式的JSON转化为字符串)
parse_json函数可以将String类型的JSON字符串解析为JSON类型。例如:
SELECT parse_json(s) is null, parse_json(s)
FROM VALUES ('null'),
('1'),
('3.14'),
('true'),
('false'),
('{"id":11,"name":"Lakehouse"}'),
('[0, 1]'),
(''),
('invalid') as t(s);
+-------------------------+------------------------------+
| (parse_json(s)) IS NULL | parse_json(s) |
+-------------------------+------------------------------+
| false | null |
| false | 1 |
| false | 3.14 |
| false | true |
| false | false |
| false | {"id":11,"name":"Lakehouse"} |
| false | [0,1] |
| true | null |
| true | null |
+-------------------------+------------------------------+
- 如果parse_json的参数为非法json字符串,则返回SQL null,is null的结果为true
- 如果输入字符串为
'null',则它会被解释为JSON null值,is null的结果为false
json_array/json_object
类似array/named_struct,可以根据已有的数据构造出对应的json类型
SELECT json_array(), json_array(NULL),json_array(NULL::int, 1, TRUE, FALSE, NULL::int, "a", 1.2, 1.3d);
+----------------+--------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| `json_array`() | `json_array`(NULL) | `json_array`(CAST(NULL AS int), 1, true, false, CAST(NULL AS int), 'a', 1.2BD, 1.3d) |
+----------------+--------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| [] | [null] | [null,1,true,false,null,"a","1.2",1.3] |
+----------------+--------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
SELECT json_object(), json_object('k', NULL), json_object('k1', json_array(1, "a"), "k2", array(1, 2, 3));
-- !query output
+-----------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| `json_object`() | `json_object`('k', NULL) | `json_object`('k1', `json_array`(1, 'a'), 'k2', `array`(1, 2, 3)) |
+-----------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| {} | {"k":null} | {"k1":[1,"a"],"k2":[1,2,3]} |
+-----------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
类型转换
在LakeHouse中,可以使用::json或CAST函数将其他类型转换为JSON类型。以下是一些类型转换的例子:
| Json | SQL |
|---|
| Object | Struct |
| Array | Array |
| String | string |
| Number | bigint/double |
| true/false | bool |
| Null | 无对应类型 |
| 无对应类型 | binary |
- 不存在于表格中的类型转换,会先将其转换为可以转换的类型(大多数情况为string类型),再转换为目标类型,例如cast(1.2 as json) 1.2为decimal类型,会先转换为string类型,进一步转换为json类型,结果是JSON '"1.2"',而不是JSON '1.2'。
- 需要注意的是cast(string as json)的语义和parse_json(string)的语义并不一致,parse_json 会尝试将 JSON 字符串解析成 JSON 对象,如果JSON格式不正确,则会生成 NULL而cast(string to json)会将字符串整体当做JSON中的string类型,所以如果您是一个json格式字符串转化时应该使用parse_json
具体案例
-- xx::json 等价于 cast(xxx as json)
SELECT 0::json;
-- !query output
+-----------------+
| CAST(0 AS json) |
+-----------------+
| 0 |
+-----------------+
SELECT 1.2F::json;
-- !query output
+--------------------+
| CAST(1.2F AS json) |
+--------------------+
| 1.2000000476837158 |
+--------------------+
SELECT 1.2::json;
-- !query output
+---------------------+
| CAST(1.2BD AS json) |
+---------------------+
| "1.2" |
+---------------------+
SELECT 's'::json;
+-------------------+
| CAST('s' AS json) |
+-------------------+
| "s" |
+-------------------+
SELECT (timestamp '2020-10-10 00:00:00') ::json;
+----------------------------------------------+
| CAST(timestamp'2020-10-10 00:00:00' AS json) |
+----------------------------------------------+
| "2020-10-10 00:00:00" |
+----------------------------------------------+
SELECT (date '2020-10-10') ::json;
+---------------------------------+
| CAST(DATE '2020-10-10' AS json) |
+---------------------------------+
| "2020-10-10" |
+---------------------------------+
SELECT array(1, 2, 3) ::json;
+--------------------------------+
| CAST(`array`(1, 2, 3) AS json) |
+--------------------------------+
| [1,2,3] |
+--------------------------------+
SELECT array(1, null, 3) ::json;
+-----------------------------------+
| CAST(`array`(1, NULL, 3) AS json) |
+-----------------------------------+
| [1,null,3] |
+-----------------------------------+
SELECT map("a", 2, "b", 4)::json, map("a", 2, "b", null) ::json;
+-----------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
| CAST(map('a', 2, 'b', 4) AS json) | CAST(map('a', 2, 'b', NULL) AS json) |
+-----------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
| {"a":2,"b":4} | {"a":2,"b":null} |
+-----------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
SELECT struct(1, 2, 3, 4)::json, struct(1, 2, 3, null::int) ::json;
+---------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------------+
| CAST(struct(1, 2, 3, 4) AS json) | CAST(struct(1, 2, 3, CAST(NULL AS int)) AS json) |
+---------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------------+
| {"col1":1,"col2":2,"col3":3,"col4":4} | {"col1":1,"col2":2,"col3":3,"col4":null} |
+---------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------------+
SELECT null::json;
+--------------------+
| CAST(NULL AS json) |
+--------------------+
| null |
+--------------------+
SELECT j::string, j::char(2), j::bigint, j::double, j::decimal(9, 4), j::boolean, j::json, j::array<int>
from values (json '123'),
(json '1.23'),
(json 'null'),
(json 'true'),
(json 'false'),
(json '"abc"'),
(json '{"a":2}'),
(json '[1,2]') t(j);
-- !query output
+-------------------+--------------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------------+--------------------+-----------------+-----------------------+
| CAST(j AS string) | CAST(j AS char(2)) | CAST(j AS bigint) | CAST(j AS double) | CAST(j AS decimal(9,4)) | CAST(j AS boolean) | CAST(j AS json) | CAST(j AS array<int>) |
+-------------------+--------------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------------+--------------------+-----------------+-----------------------+
| 123 | 12 | 123 | 123.0 | 123.0000 | true | 123 | null |
| 1.23 | 1. | 1 | 1.23 | 1.2300 | true | 1.23 | null |
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null |
| true | tr | 1 | 1.0 | 1.0000 | true | true | null |
| false | fa | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0000 | false | false | null |
| abc | ab | null | null | null | null | "abc" | null |
| {"a":2} | {" | null | null | null | null | {"a":2} | null |
| [1,2] | [1 | null | null | null | null | [1,2] | [1,2] |
+-------------------+--------------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------------+--------------------+-----------------+-----------------------+
需要注意的是,cast(string as json)和parse_json(string)的语义并不一致。parse_json会尝试将JSON字符串解析成JSON对象,如果JSON格式不正确,则会生成NULL;而cast(string to json)会将字符串整体当做JSON中的string类型。
SELECT parse_json(s), s::json, s::json::string
FROM VALUES ('{"id":11, "name": "Lakehouse"}') as t(s);
+------------------------------+----------------------------------------+---------------------------------+
| parse_json(s) | CAST(s AS json) | CAST(CAST(s AS json) AS string) |
+------------------------------+----------------------------------------+---------------------------------+
| {"id":11,"name":"Lakehouse"} | "{\"id\":11, \"name\": \"Lakehouse\"}" | {"id":11, "name": "Lakehouse"} |
+------------------------------+----------------------------------------+---------------------------------+
使用SDK(igs/bulkload)写入JSON
Lakehouse 支持给 JSON 类型的列写入 String 类型的字符串,系统在导入的时候会自动将字符串解析成 JSON 类型,如果用户输入了不符合 JSON 规范或者 CZ 不支持的 JSON 字符串,系统会报错并停止导入。
导出JSON数据
Lakehouse 支持以字符串的形式导出 JSON 数据。
查询JSON数据
查询JSON数据需要使用json_extract系列函数,通过JSON path获取需要的数据。以下是一些查询JSON数据的例子:
- json_extract
- json_extract_boolean
- json_extract_float
- json_extract_double
- json_extract_int
- json_extract_bigint
- json_extract_string
- json_extract_date
- json_extract_timestamp
json path规范
json_extract的第二个参数为json path,可以参考json path规范
- "$"表示根元素
- ".key"或者"['key']" 用来查找json object中的key。特殊的,"[*]"表示获取所有的value,要求必须是单引号
- "[index]" 用来根据index访问 json array的元素,起始值为0。特殊的,"[*]"表示所有的元素
SELECT json_extract(j, "$[0]"),
json_extract(j, "$[1]"),
json_extract(j, "$[*]")
FROM VALUES (JSON '["a", 1, null]') as t(j);
+-------------------------+-------------------------+-------------------------+
| json_extract(j, '$[0]') | json_extract(j, '$[1]') | json_extract(j, '$[*]') |
+-------------------------+-------------------------+-------------------------+
| "a" | 1 | ["a",1,null] |
+-------------------------+-------------------------+-------------------------+
SELECT json_extract(j, "$.key"),
json_extract(j, "$['key.with.dot']"),
json_extract(j, "$[*]")
FROM VALUES (JSON '{"key":1, "key.with.dot":2}') as t(j);
+--------------------------+----------------------------------------+-------------------------+
| json_extract(j, '$.key') | json_extract(j, '$[\'key.with.dot\']') | json_extract(j, '$[*]') |
+--------------------------+----------------------------------------+-------------------------+
| 1 | 2 | [1,2] |
+--------------------------+----------------------------------------+-------------------------+
SELECT json_extract(j, '$.*.city'),
json_extract(j, '$.phoneNumbers[*]'),
json_extract(j, '$.phoneNumbers[*].extra'),
json_extract(j, '$.phoneNumbers[*].extra[*]'),
json_extract(j, '$.*[*].extra[*]')
FROM (SELECT parse_json(s) as j
FROM VALUES ('{ "firstName": "John", "lastName": "doe", "age": 26, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [] } ] }'),
('{ "firstName": "Ada", "lastName": "doe", "age": 20, "address": { "streetAddress": "naist street", "city": "Nara", "postalCode": "630-0192" }, "address2": {"city": "NewYork"}, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "iPhone", "number": "0123-4567-8888" }, { "type": "home", "number": "0123-4567-8910", "extra": [1,2,3] } ] }'),
('{} ') as t(s));
+-----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------+------------------------------------+
| json_extract(j, '$.*.city') | json_extract(j, '$.phoneNumbers[*]') | json_extract(j, '$.phoneNumbers[*].extra') | json_extract(j, '$.phoneNumbers[*].extra[*]') | json_extract(j, '$.*[*].extra[*]') |
+-----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------+------------------------------------+
| ["Nara"] | [{"number":"0123-4567-8888","type":"iPhone"},{"extra":[],"number":"0123-4567-8910","type":"home"}] | [[]] | null | null |
| ["Nara","NewYork"] | [{"number":"0123-4567-8888","type":"iPhone"},{"extra":[1,2,3],"number":"0123-4567-8910","type":"home"}] | [[1,2,3]] | [1,2,3] | [1,2,3] |
| null | null | null | null | null |
+-----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------+------------------------------------+
其他JSON函数
json_valid用来验证一个string类型的数据是否可以转换为json类型
SELECT json_valid('hello'),
json_valid('"hello"'),
json_valid('null'),
json_valid('{}'),
json_valid('[]'),
json_valid('{"a": "b"}'),
json_valid('[1, "a"]');
+---------------------+-----------------------+--------------------+------------------+------------------+--------------------------+------------------------+
| json_valid('hello') | json_valid('"hello"') | json_valid('null') | json_valid('{}') | json_valid('[]') | json_valid('{"a": "b"}') | json_valid('[1, "a"]') |
+---------------------+-----------------------+--------------------+------------------+------------------+--------------------------+------------------------+
| false | true | true | true | true | true | true |
+---------------------+-----------------------+--------------------+------------------+------------------+--------------------------+------------------------+
性能对比
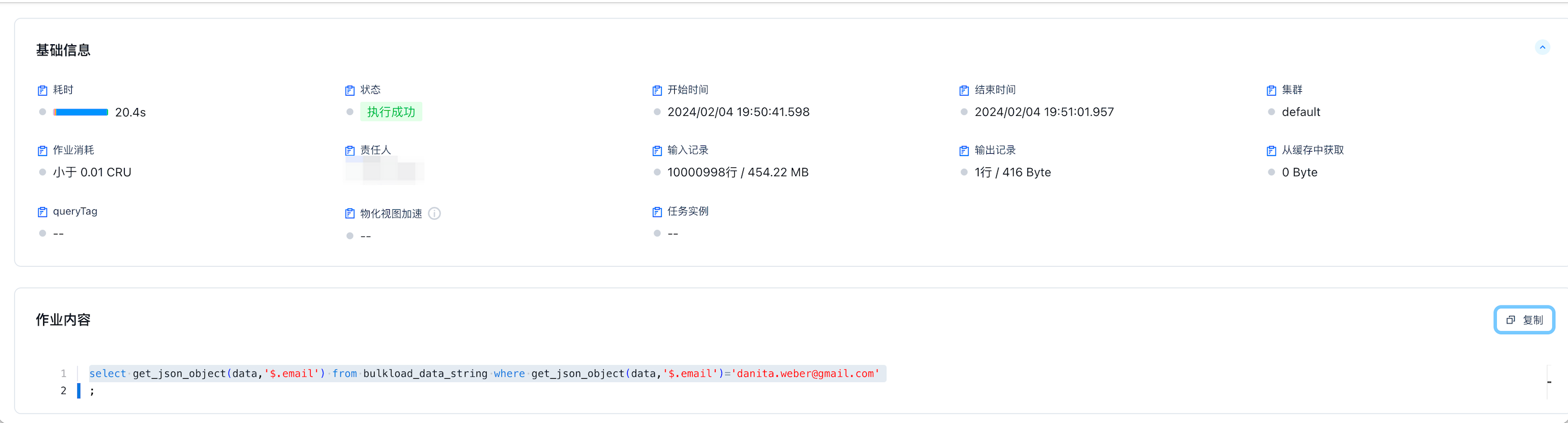
构造的数据为1000多万条这样格式{"address":"89695 Lind Common, Kellymouth, AK 61747","email":"``danita.weber@gmail.com``","name":"Golda Shields"},使用where进行过滤查询
使用string查询,执行时间为20.4s。
create table bulkload_data_string(data string);
select get_json_object(data,'$.email') from bulkload_data_string where get_json_object(data,'$.email')='danita.weber@gmail.com'
;
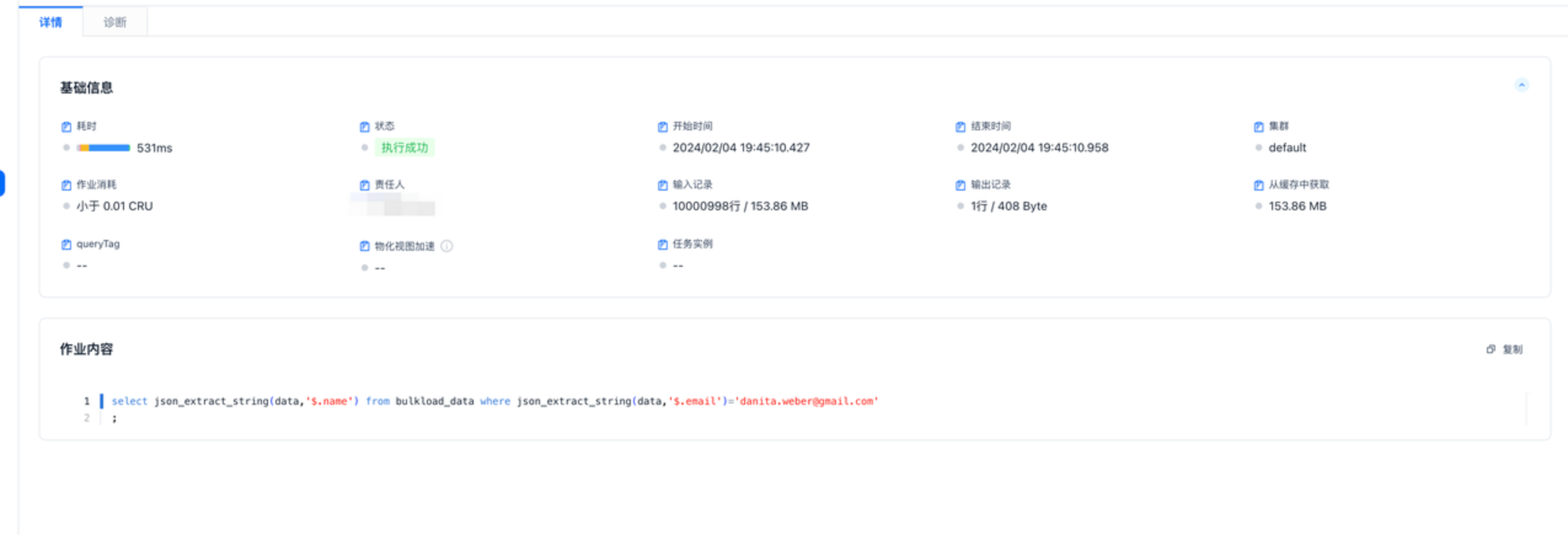
使用json存储数据执行时间为531ms,因为读取的时候进行列裁剪数据大小也会减少,如下图只需要读取153MB数据,string类型需要全量读取454MB数据
create table bulkload_data(json string);
select json_extract_string(data,'$.name') from bulkload_data where json_extract_string(data,'$.email')='danita.weber@gmail.com'
;